Puccinia hemerocallidis Life Cycle ImagesClick on any image for a larger view, and use your browser's "Back" button to return here |
||
|
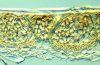
Telia: Telia are formed on the adaxial surface of daylily leaves. They first appear as honey-brown or chocolate-brown raised spots and soon develop a blackish crust appearance. Telia may be isolated, or crowded and fused to each other. Click on thumbnail for a larger image. | ||
|
Telium section: Teliospores are produced in small chambers surrounded by specialized mycelium, paraphyses. Individual locules are surrounded by paraphyses and the teliospores contained in them compose the telia. Click on thumbnail for a larger image. |
||
|
Teliospores: Teliospores are mostly two-celled, sometimes one-celled, and formed from a teliospore mother cell in the base of the telium. The teliospores bear a short pedicel at the base. Click on thumbnail for a larger image. |
||
|
Teliospore germination: Teliospores germinate after a period of dormancy. Cold or freezing temperature seems to be mandatory to break the dormancy. When the teliospores germinate, crustose telia appear cottony due to the production of elongate basidia. Click on thumbnail for a larger image. |
||
|
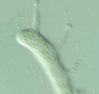
Basidium: The basidium first appears as an elongate tube arising from each cell of the teliospore. The top-most portion of the basidium soon becomes partitioned and a short sterigma arises from each of four partitioned cells. A basidiospore is formed at the tip of the sterigma. Click on the thumbnail for a larger image. To enlarge even further, click here |
||
|
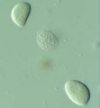
Basidiospores: Mature basidiospores are kidney-shaped and thin-walled. Click on thumbnail for a larger image. |
||
|
Spermogonia: Seven to ten days after the basidiospore infection, spermogonia appear on both surfaces of the infected leaves of Patrinia villosa. The spermogonia are isolated or crowded and appear yellowish orange with masses of spermatia in a sugary fluid. The areas in which the fungal mycelium extends appear pale yellowish green. Click on thumbnail for a larger image. |
||
|
Aecia: Aecia are produced mostly on abaxial surface of the infected Patrinia leaves. Click on thumbnail for a larger image. |
||
|
Aeciospores: Aeciospores are produced in a chain. They are subglobose, thin-walled and warted. Even though the spore wall is colorless, the spores appear yellowish due to carotenoid pigments contained in the cytoplasm. Click on thumbnail for a larger image. |
||
|
Uredinium section: Unlike the telium, the uredinium is not organized into a small chamber by surrounding paraphyses. Urediniospores are produced on a short pedicel from the sporogenous cells in the base layer of the uredinium. Click on thumbnail for a larger image. |
||
|
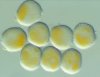
Urediniospores: Urediniospores are subglobose to broadly ellipsoid. The wall is colorless and bears spines on the entire surface. Click on thumbnail for a larger image. |
||
|
©2002-14 Images and text by Dr. Y. Ono, Japan, used here with permission. |
||